Alcohol are derivatives of hydrocarbons, one are more of the hydrogen atoms have been replace by a hydroxyl (OH functional group). Alcohol can be a really terrible thing when it is abused. The problems it causes do not just damage the user but their friends, family, and society as a whole.
ALCOHOLISM:
Alcoholism is a serious addiction that can be described as an irresistible urge to consume alcohol. It is one of the serious social problems which is rapidly increasing in every year.
It has four distinct symptoms
- A strong desire to drink in any circumstances.
- Loss of control while drinking.
- Withdrawal symptoms.
- Need to drink greater amounts of alcohol.

CAUSES OF ALCOHOLISM
- Genetics – some people are literally born with genes predisposing them to alcoholism.
- Family issues, including the loss of family ties or abuse by a family member, can cause alcoholism.
- Personality disorders
- Peer pressure
- Cultural values can also lead to the same end result. For instance, some nations, cultures, and people consider it ok for children to drink a little alcohol, whereas others abhor such a notion.
ALCOHOL ABUSE VS. ALCOHOL DEPENDENCE
Alcohol abuse refers to the recurrent use of alcohol to such an extent that it impairs function, results in injury, or endangers others. As an example, a person who doesn’t drink during the week but goes out with friends every weekend, binges, and then drives home drunk is an abuser of alcohol.
Were as alcohol dependence, refers to a compulsive and excessive state of alcohol consumption, physical and mental impairment as a result of this consumption, tolerance to alcohol, and development of withdrawal symptoms upon reduction of its intake.
Tolerance, by the way, simply means that an individual needs more alcohol to produce the same effect as before or is unaffected by large amounts of alcohol that would impair a normal user.
Stages of Alcoholism
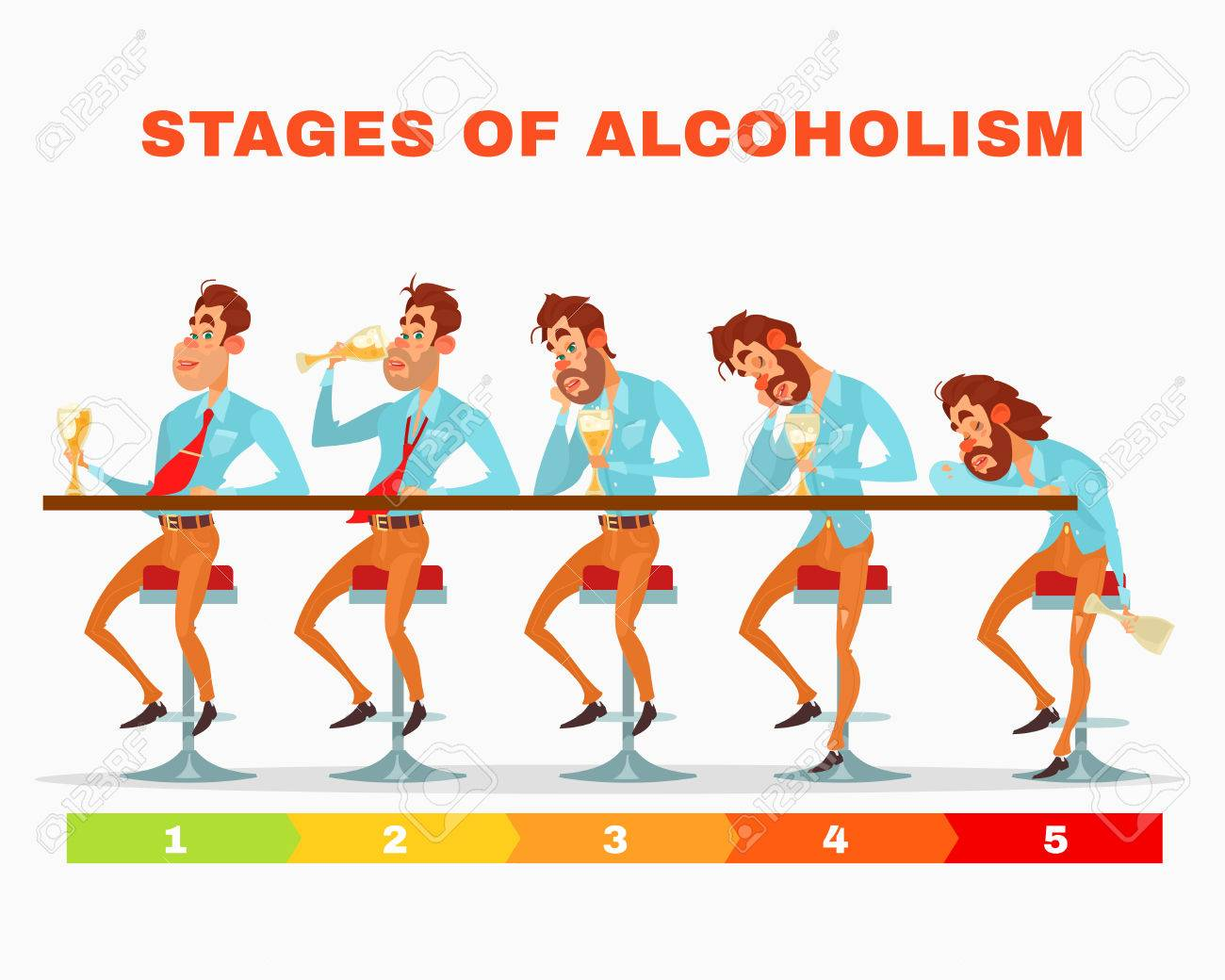
STAGE 1: OCCASIONAL ABUSE AND BINGE DRINKING
- The first stage of alcoholism is a general experimentation with alcohol. These drinkers may be new to different forms of alcohol and likely to test their limits. This experimental stage is commonly seen in young adults.
- These experimental drinkers also frequently engage in binge drinking. While they may not drink regularly, they consume exceptionally large amounts of alcohol at one time.
- Drinking large amounts of alcohol at one time is dangerous, and can even lead to coma or death. Further more you may become dependent on the feeling you get from drinking and find that these episodes increase in frequency.
STAGE 2: INCREASED DRINKING
- Drinkers leave the experimental stage when their alcohol consumption becomes more frequent Instead of just drinking at parties once in a while, you may find yourself drinking every weekend.
- Regular alcohol use is different from moderate drinking. There is usually a higher emotional attachment to it.
- A moderate drinker might pair a glass of wine with a meal, while a regular drinker uses alcohol to feel good in general. As increased drinking continues, you become more dependent on alcohol and are at risk of developing alcoholism.
STAGE 3: PROBLEM DRINKING
- Frequent, uncontrolled alcohol abuse eventually leads to problem drinking. While any form of alcohol abuse is problematic, the term “problem drinker” refers to someone who starts experiencing the impacts of their habit.
- You may become more depressed, more anxious, or start losing sleep. You may start to feel sick from heavy drinking, but enjoy its effects too much to care. Many drinkers at this stage are more likely to drink and drive or experience legal troubles as a result of their drinking.
- There are also specific social changes related to problem drinking. These include:
- Relationship issues
- Decreased social activity because of erratic behaviour
- Sudden change in friends
- Difficulty conversing with strangers
STAGE 4: ALCOHOL DEPENDENCE
- Alcoholism has two facets: Dependence and Addiction. It’s possible for a person to be dependent on alcohol, but not yet addicted.
- Dependence forms after the problem drinking stage. At this point, you have an attachment to alcohol that has taken over your regular routine. You’re aware of the adverse effects, but no longer have control over your alcohol consumption.
- Alcohol dependence also means that you have developed a tolerance to drinking. As a result, you may have to drink larger quantities to get “buzzed” or drunk. Increased drinking has more damaging effects on the body.
- Another characteristic of dependence is withdrawal. As you sober up, you may feel undesirable symptoms such as:
- Nausea that is unrelated to a hangover
- Body tremors
- Sweating
- Severe irritability
- A racing heart
- Trouble sleeping
STAGE 5: ADDICTION AND ALCOHOLISM
- The final stage of alcoholism is addiction. At this stage, you no longer want to drink just for pleasure. Alcohol addiction is characterized by a physical and psychological need to drink.
- People with alcohol addiction physically crave the substance and are often inconsolable until they start drinking again. They may be addicted to other drugs as well.
- Compulsive behaviours are prominent in addiction, and people with alcohol addiction often drink whenever and wherever they desire.
CONSEQUENCES OF ALCOHOLISM

TREATMENT
Before starting the treatment process, a person must first recognize their condition and have a desire to quit drinking. Sometimes, an individual may acknowledge they have a drinking problem on their own. Other times, family members or friends may stage an alcohol intervention.
Some of the treatments are
- Detoxification
- Inpatient Rehab
- Counselling
- Behaviour modification
- Medication
CONCEPT IN AYURVEDA
- According to Ayurveda, inappropriate usage of alcohol for long duration leads to development of the disease Madatyaya. It is a sannipataja vyadhi and mainly vitiates Ojas.
- It is also characterised by excessive accumulation of morbid doshas in the body. It is not just alcohol intoxication, dependence or withdrawal state, but it is the condition where multiple systemic dysfunctions are involved. Neurological, gastro – hepatic and cardio pulmonary manifestations are the commonest features seen in the patients of Madatyaya which is also similar to the descriptions of alcoholism.
- It is classified into Vatika, Paittika, kaphaja, sannipataja (based on Doshic predominance), Panatyaya, paramada, Panajeernaa, Panavibhrama, Dhwamsaka and Vikshaya.
DIFFERENT STAGES OF ALCOHOLIC INTOXICATION
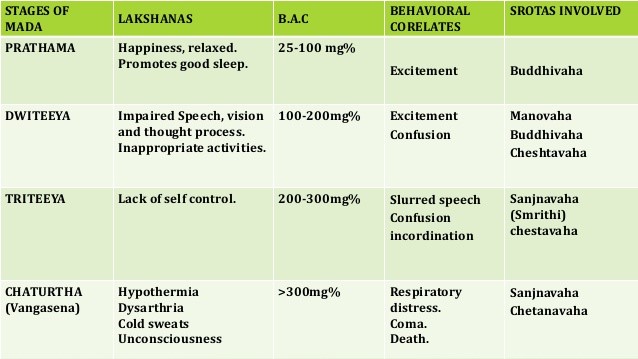
Ayurveda plays an important role in management of adverse effects caused by taking excess of alcohol and also management of alcohol withdrawal symptoms through various Panchakarma procedures along with Samsarjana karma.
Dr.Gayatri Priyanka.Mullapudi
MD( Ayu) PG.D in yoga,
Associate Centre Head-Madinaguda
Travancore Ayurveda.












