Welcome to An Ayurvedic Detox retreat program of Travancore Ayurveda.
Human body will get accumulated with doshas or toxins in the long run of life and it is advised to clear these doshas from the body time to time. This process is generally known as detoxification. In Ayurveda, there are five shodhana therapies said for the detoxification of human body and one among them is Raktamoksha.
Raktamoksha as the term indicates means the letting out of blood. As the major transport medium in the body, blood will receive all types of doshas from different parts of body. During the course of time these doshas will be removed from the body through the normal excretory organs and with the help of liver, spleen, kidneys and skin. But in some or other cases, when the dosha levels in blood are above the limit, it will toxify the blood itself and this blood is known as dushta raktha. This mostly happens in local body parts as the blood tries to eliminate its doshas by collecting and segregating them in any specific body part. These in turn will make that specific body area vitiated of doshas and later will show some symptoms and then manifests as a disease.
This can happen in the other way also. Due to any reason when a disease manifest in any part of the body, there is a chance that the blood flowing to that area will get slowed. And the stagnated blood in that specific area will get the doshas vitiated and there by leading to formation of dushta raktha. This mainly happens in the secondary or tertiary stage of that disease, where the major cause of raktha dushti will be the main disease itself. This type of raktha dushti may persist even after curing the main disease also. In either of these cases the dushta rakta has to be purified or let out of the body.
Ayurveda mentions different methods for Raktamoksha according to the site and type of dosha dushti. Shringa, Jalooka and Alabu are the main procedures said according to the type of dosha dushti respectively done in Vata, Pitha and Kapha dosha dushti. Other methods according to the site of dosha dushti include siravedha, prachana, etc
Shringa / Blood letting with a horn
In ancient times as described in samhitas the horn or animals were used to remove the blood from the body parts. The inside of cow’s or deer’s horn with specific length, is carved to hollow and its broad base is pressed to the part of the body where an incision is made previously. Blood is then sucked in to the horn through the narrow end of horn.
This method is now modernised with the use of cups and suction pumps. Cups made of glass were used previously, which needs to be sterilised after every use. But nowadays disposable cups made of plastic are used widely. This helps in keeping high standards of hygiene and infection prevention.
The part of the body from where the blood need to be removed is cleaned and disinfected thoroughly and small incisions are made with surgical blade. Then the wide mouth of cup is fixed on the area and the air inside the cup is sucked out with the help of a suction pump. A low pressure created inside the cups will then drain the blood from the body to the cups. Once enough blood is drained, cups are removed and the area is cleaned and a bandage is done if needed.
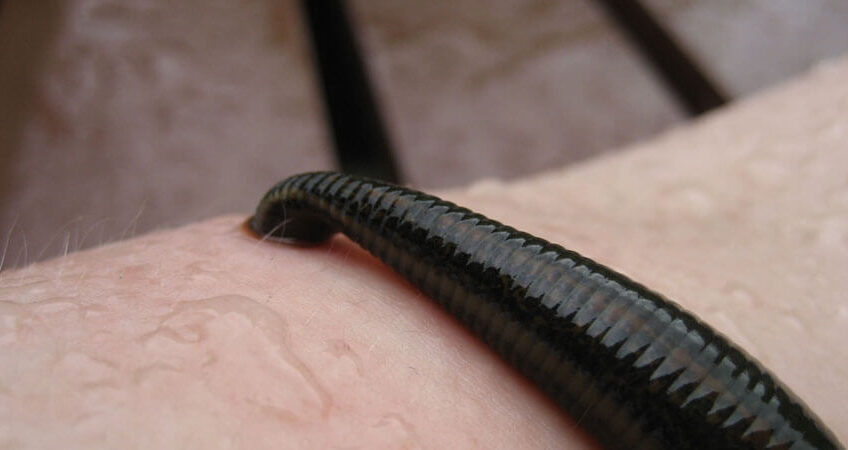
Jalookavacharana / Leech therapy
Jalooka or Leach is a small earth worm like animal with suckers and is coming under the family Hirudinidae. From the ancient times itself it is widely used in the raktamoksha therapies. Since leech always lives in watery areas and is cold or sheetha in nature it is best used in pitha dosha dushti conditions. There are many types of leeches seen around but only five types of them are to be used in medical leech therapy. Other types are poisonous and when used in humans may cause adverse effects and health issues.
The area where leeches are applied is cleaned properly and made slightly rough. Afterwards leeches are applied directly on that area. Leech will bite on the area and will start sucking the blood immediately using its suckers. It says that leech has an ability to differentiate between shudha and dushta raktha and it sucks only dushta raktha. If the leech starts to suck shudha rakta some symptoms like itching or pain will develop in the body and then we have to remove the leech from the body. If otherwise after sucking sufficient blood the leech will drop off by itself. As the saliva of leech contains an anticoagulant enzyme known as hirudin, blood will be oozing out of the wound even after the leech is dropped off. The wound is then cleaned and dressed with medicines that promotes blood clotting and is bandaged tightly.
Alabu / Hot cupping
This is mainly done in Kapha dosha dushti. A small lighted candle or oil wick is placed on the pre sterilised and incised body part. This is then covered with the dry shell of bottle guard. The flame inside creates a low pressure and it will then drain the blood out from the body though the incision. Even though this is not widely practiced nowadays, this can be compared as hot cupping.
Prachana
This is done mainly in those conditions where the dosha dushti is spread on a wide area of skin like that in eczema. Multiple small pricks or incisions are made on the skin with a sharp needle or surgical blade. Dushta rakta which is stagnated in that area of skin will be let out. This can also be done in alopecia where the skin gets toughened with dosha dusti.
Siravedha / Venipuncture
Sira vedha or direct puncturing of vein is done in many diseases related to muscles, nerves and joints. Siravedha is as important as Vasti in General medicine and is considered as fifty percentage of treatments by Ayurvedic surgeons. There are some specific sites in the body where the veins are prominently seen in the periphery. These are cut with special surgical instruments and the blood is let out. The site, depth and size of cut etc are described and are different according to the disease condition. Nowadays sterile injection needles with different gauges are used to remove blood by this method. The site of siravedha is to be decided by the physician adhering to the text books. Post treatment, the area is cleaned with antiseptic medicines and tight bandages are done if needed.
Indications
Raktamoksha is indicated in a variety of diseases. Skin diseases like eczema, psoriasis etc, diabetic ulcers, joint swellings or edema, external anal abcess, vericoce veins are some diseases where raktamoksha is very effective. It is also used in diseases of eye, some type of tumors and polyps, as add on treatment in neurological conditions etc. Whenever the raksha is getting dushti either primarily or secondarily, raktamoksha therapy plays an important role in managing it.
In most cases the sthanika or local shodhana therapies are administered after the abhyanthara or internal shodhana. So other shodhana karmas like vamana, virechana etc are advised, as the case may be, before doing the rakthamoksha therapy. This helps to prevent the recurrence of the disease and for a long lasting benefit of treatments.
Dr. Nizamudheen A M ,B.A.M.S
Centre Head -Sainikpuri
Travancore Ayurveda